What are Operators, Operands, and Expressions?Types of Operators Based on Operand CountStandard TradingView OperatorsAssignment OperatorArithmetic OperatorsAccessing Historical DataConditional Logic in Pine ScriptBoolean Operators in TradingViewCreating Custom FunctionsOperator Precedence in TradingViewCitations
In TradingView, operators are essential for coding scripts. But what exactly are operators, and how do they work?
What are Operators, Operands, and Expressions?
An operator is a code element that performs an action on one or more values (called operands) to produce a new value. For example, in
5 + 3, the + is the operator, and 5 and 3 are operands. The result is 8, which is the new value created by the operator.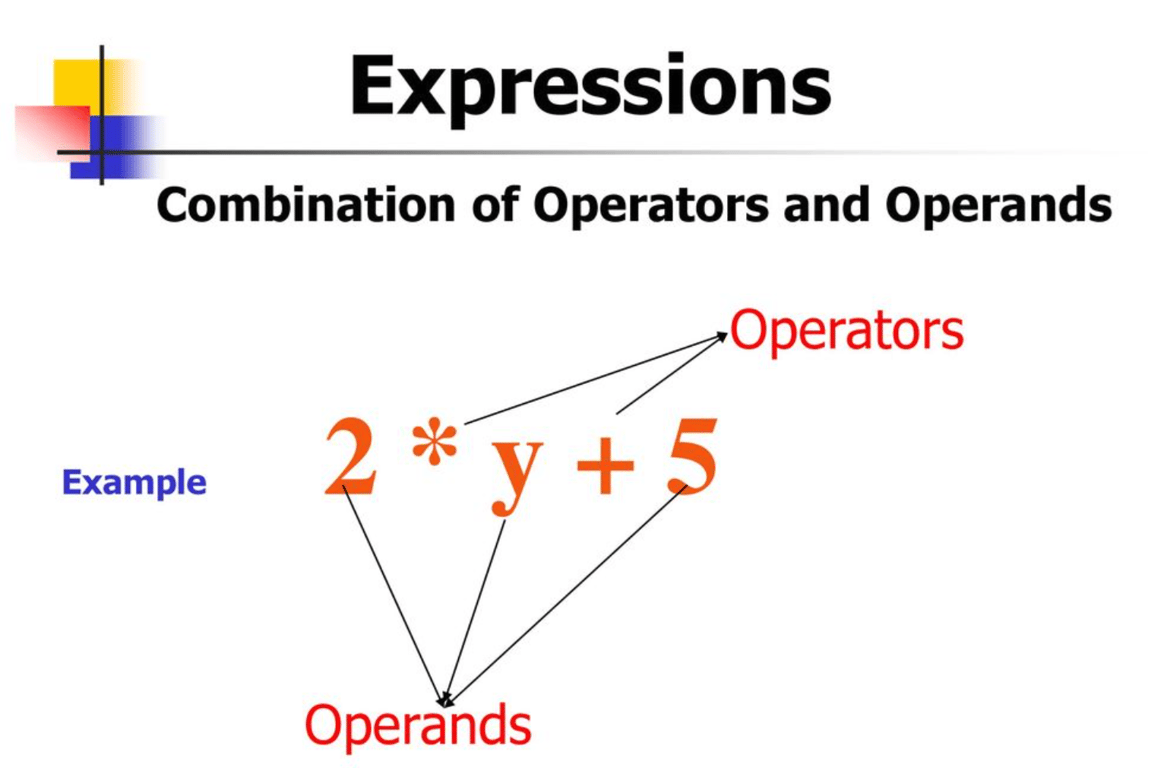
A statement can contain multiple operators, and their evaluation order depends on their priority. An expression refers to a piece of code that returns a value, often containing operators. For instance:
45 * 9.12returns410.4
ema(close, 20)returns the 20-period Exponential Moving Average
(high - low) / 2returns half of the bar's range
Types of Operators Based on Operand Count
Operators in TradingView can be classified by how many operands they act upon:
- Unary operators: Operate on one value (e.g.,
closereturns the negative closing price).
- Binary operators: Operate on two values (e.g.,
close > opencompares closing and opening prices).
- Ternary operator: Takes three operands (e.g., the conditional ternary operator
?:, which acts like an if/else statement).
Standard TradingView Operators
Assignment Operator
The assignment operator (
=) stores values in variables or assigns values to function arguments.Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators include addition (
+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and modulus (%). These operators allow you to perform basic mathematical operations. Additionally, strings can be concatenated using the + operator.Accessing Historical Data
Historical data is crucial for most scripts. You can retrieve values from previous bars using the history referencing operator (
[ ]). This operator works with built-in variables, custom variables, functions, and more.Conditional Logic in Pine Script
While TradingView lacks traditional if/else statements, you can mimic this behavior using:
- Ternary operator (
?:): This acts like a concise if/else statement by returning one value if a condition is true and another if it’s false.
Boolean Operators in TradingView
Boolean values (true/false) are handled using comparison and logical operators:
- Comparison operators: Compare numbers (e.g.,
>,<,==) to return true/false.
- Logical operators: Combine multiple true/false expressions (e.g.,
and,or,not) into a single boolean result.
Creating Custom Functions
You can create custom functions using the function declaration operator (
=>). This allows you to define reusable code blocks for both single-line and multi-line functions.Operator Precedence in TradingView
Operator precedence determines the order in which operations are performed. For example:
- History referencing (
[])
- Unary operators (
+,,not)
- Multiplication/division/modulus (
,/,%)
- Addition/subtraction (
+,)
- Comparison operators (
>,<,>=,<=)
- Equality operators (
==,!=)
- Logical conjunction (
and)
- Logical disjunction (
or)
- Ternary operator (
?:)
Parentheses can be used to change this default precedence.